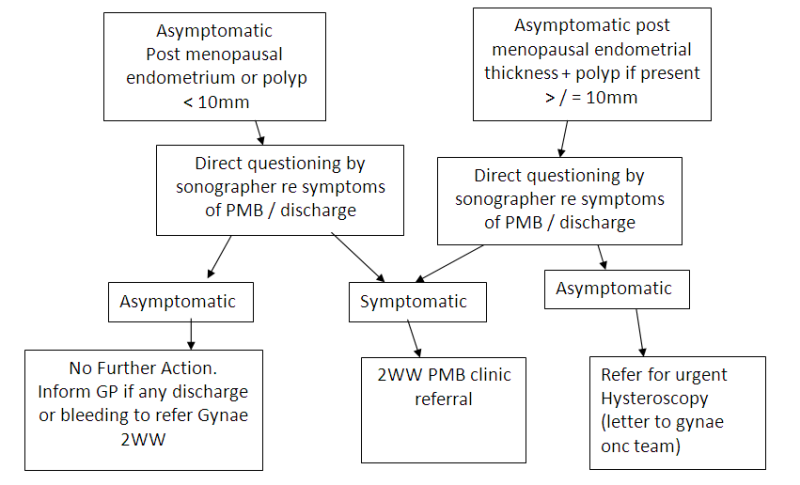
Endometrial thickness must be evaluated together with endometrial morphology as well as risk factors for malignancy when considering endometrial sampling.
Thickening of the womb lining after menopause no bleeding.
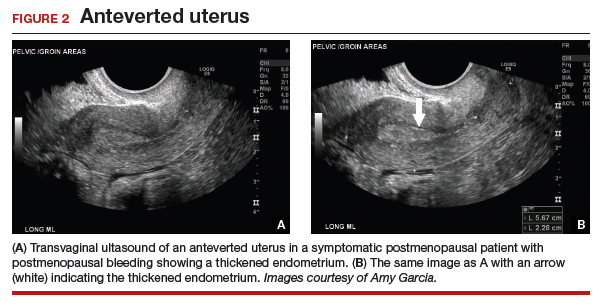
Endometrium thickening may cause bleeding after menopause but even without bleeding the possibility of endometrial cancer cannot be ruled out.
Endometrial hyperplasia is a non cancerous benign condition where the lining of the womb becomes thicker.
You have a higher risk of developing womb cancer if you have this thickening especially if the extra lining cells are abnormal.
As a result the endometrium gets thicker and can bleed.
This is the layer of cells that line the inside of your uterus when your endometrium thickens it can lead to unusual bleeding.
Endometrial hyperplasia is caused by a presence of excessive cells in the lining of the uterus.
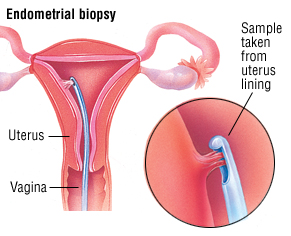
Confirmation may be done using endometrial biopsy.
Endometrial hyperplasia refers to the thickening of the endometrium.
Endometrial hyperplasia thickening of the uterine lining.
If a woman who has already gone through menopause suddenly has bleeding and an ultrasound test shows that her uterine lining is thicker than 4 to 5 mm she may need an endometrial biopsy to make.